African Forest Elephant
African Forest Elephant Facts
| Size | 6-9 feet (180-280 cm) |
| Speed | Up to 24 mph (39 km/h) |
| Weight | 2-4 tons |
| Lifespan | 60-70 years |
| Food | Plants, fruits, roots |
| Predators | Leopards |
| Habitat | African rain forests |
| Order | Proboscidea |
| Family | Elephantidae |
| Scientific name | Loxodonta cyclotis |
| Characteristics | Trunk, tusks, small ears |
Main Characteristics
The African forest elephant is the smallest of all elephants - and like the “little brother” of the African bush elephant. It is smaller and lighter, with smaller ears and shorter tusks. It also has a different habitat. It does not live in the savanna, but in tropical rainforests. African forest elephants are considered an endangered animal species.

Distribution and Habitat
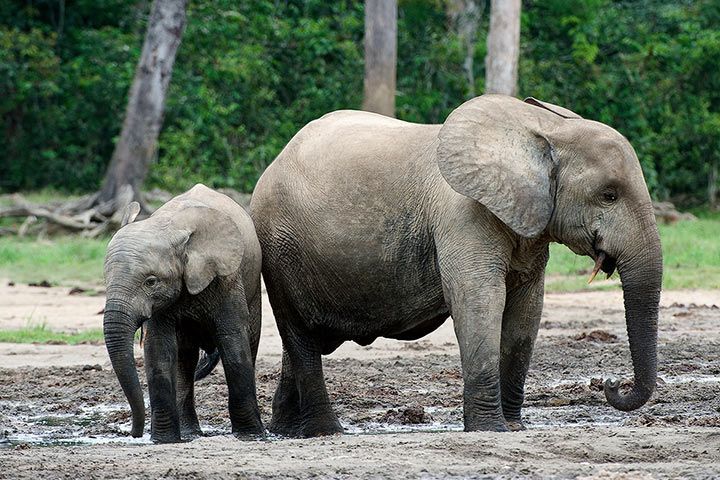
The African forest elephant lives in the Congo Basin in Central Africa and in the rainforests of West Africa. Its habitat is swampy, damp forests. A frequent question is: Are there any forest elephants in the Amazon rainforest? That's a good question, but the answer is simple: No. They only live in Africa. The Amazon rainforest is located in South America.
Life Style
African forest elephants form small, social groups. They're active during the day and walk for miles in the forest. As they move, they unintentionally squash the plants, flattening them out. This creates paths that can be as wide as three feet (one meter). The paths form a vast network with plenty of intersections that serve as gathering spots where the elephants come together.
Unfortunately, there is not much more information available about the African forest elephant. Understanding its lifestyle is a challenging task for researchers due to constant conflicts among humans in the surroundings. This makes it unsafe for researchers to stay.
Anatomy and Appearance
Size and Weight
The African forest elephant is the smallest of all elephant species. It has a shoulder height of 6-9 feet (180-280 cm) and grows 3-10 feet (1-3 meters) in length. Its weight is 2-4 tons.
Tusks
Both male and female African forest elephants have tusks. They are rather straight and thin, but very hard.
Skin
The skin of African forest elephants is smooth and slightly darker than that of African bush elephants.
Ears
The forest elephant has small, oval-shaped ears.
Toes
Forest elephants have five toes on the forefoot and four on the hind foot.
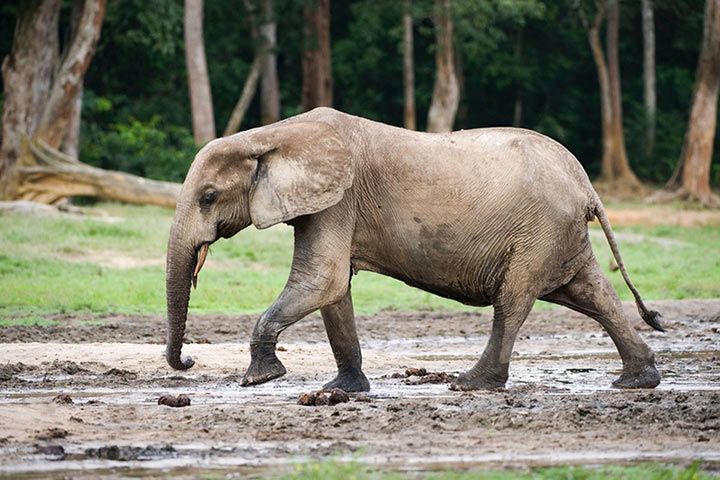

African Bush Elephant or African Forest Elephant – What is the difference?
• Species of its Own
Both elephant species live in Africa and are closely related to each other. Yet, the African forest elephant is not the “smaller brother” of the tall African elephant. It is a species of its own, which has developed differently from the African elephant during the last three to five million years.
• Habitat
While the African elephant lives in steppes and savannas, the African forest elephant prefers the dense tropical jungle. This is why it is significantly smaller. It would be difficult for a tall elephant to move around in dense forests.
• Anatomy and Appearance
The tusks of African forest elephants are straighter and less curved. If you compare them to those of African and Indian elephants, the tusks appear a bit like toothpicks. Yet, the tusks of older elephants can be so long that they touch the ground. The ears are smaller and more oval. The number of toes is also different. The African forest elephant has more toenails: five at the fore foot and four at the hind foot. The African has four at the fore foot and three at the hind foot.
• Predators
The African forest elephant's habitat is different to the habitat of leopards, hyenas and lions. While these live mostly in open savannas and steppes, its home is the forest. So it is usually spared from these predators. Its only natural enemy is the leopard.
Diet
Forest elephants feed primarily on fruits, but they also eat plants. They also love mineral, salty water. To get it, they have a trick: First, they dig holes in the ground with their legs and tusks - up to 13 feet (4 meters) deep. Then they wait. As the water seeps in, it carries with it the dissolved minerals from the surrounding soil, creating a refreshing drink!
Behavior
Are African Forest Elephants dangerous?
It's important to note that African forest elephants can be dangerous, but it's primarily because of human impact. As we continue to shrink their habitat, they are forced to venture into areas where people reside. They end up munching on crops and become angry when we try to chase them off.
Migration
African forest elephants migrate during the dry season. They search for places with enough water, such as rivers and other water sources.
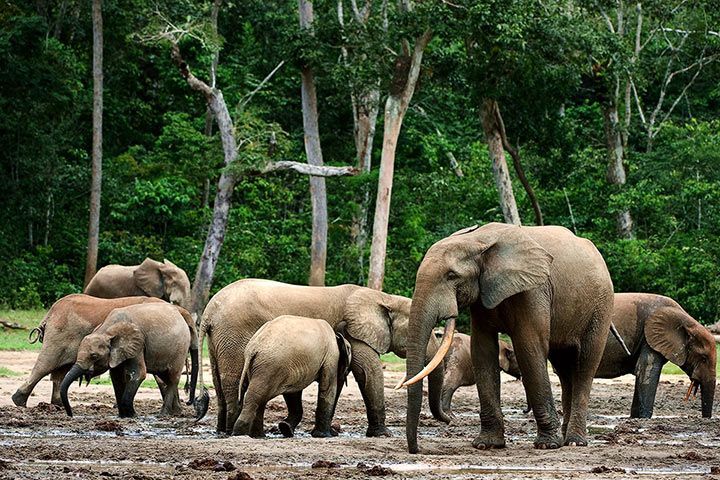

Life Span
The African forest elephant has a life expectancy of 60-70 years. However, its actual life cycle is much shorter, because the animals are being hunted by poachers. That's why they usually die much earlier.
Enemies and Threats
Natural Enemies
African forest elephants don't have many enemies. The only predator it has to fear is the leopard.
Human Impact
Humans are the biggest threat to forest elephants.
Poaching and Hunting
Hunting and killing African forest elephants is strictly prohibited, but unfortunately, the animals are still being killed by poachers and hunters. Their meat is a source of food (so-called “bushmeat”) and their tusks are more dense than those of the African bush elephant, making them more valuable and fetching higher prices. The poachers have an “easy job” because they can hide well in the rainforest and are rarely discovered. Elephants that have been injured but not killed by poachers are often discovered too late in the dense forest.
Habitat Loss
Forest elephants are facing a major threat due to the deforestation of tropical rainforests. The construction of roads is shrinking their habitat even more.
Population
How many African forest elephants are left? According to the WWF, there are less than 100,000 African forest elephants remaining. Every year their numbers shrink by 10-18%. At the same time, they have a slower reproduction rate than the African bush elephant. Instead of giving birth every 3.5 to 4.5 years, they only do so every 5-6 years. It is estimated that it would take over 80 years to compensate for the last 10 years decline through reproductive initiatives.
Conservation Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the African forest elephant is endangered and labeled as “threatened with extinction”.
Importance to the Ecosystem
African forest elephants play a crucial role in the ecosystem as they act like nature's gardeners. They eat a lot of fruits and disperse the seeds through their droppings. In this way, they contribute to the growth of numerous new plants. Plus, they give trees a helping hand in growing. As they wander around the dense rainforest, they stomp on plants and young trees. But that's actually a good thing. It creates open spaces in the forest and allows more sunlight to reach the shadowy areas. This means the other trees get more light and can grow even bigger.
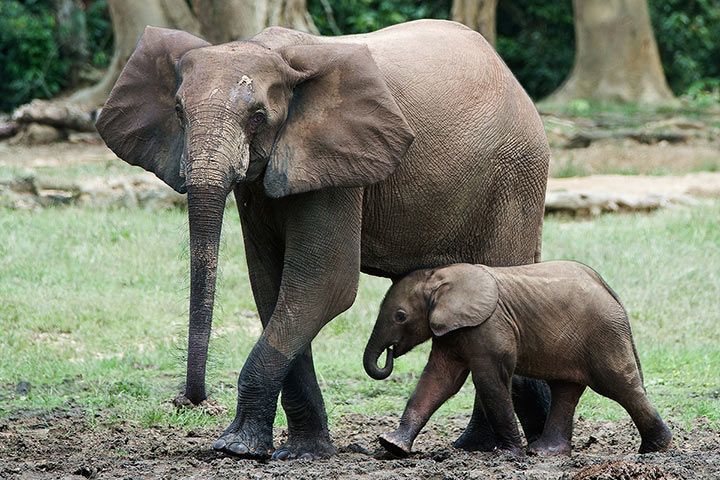

Reproduction
Females begin to reproduce at 10-12 years of age. Males don't start to reproduce until they are 25-30 years old. The gestation period of African forest elephants is similar to that of all elephant species: around 660 days. However, they only give birth every 5-6 years. When born, the baby elephant weighs around 100 kg and can start running within minutes. The mother will nurse the baby for up to five years before their tusks begin to grow.
Fun Facts
European Forest Elephant
In Europe, forest elephants existed between 33,000 and 900,000 years ago. While today's species live in the warm, tropical climate of Africa and Asia, their European relatives somehow managed to adapt to colder temperatures. Scientists think that it had at least some hair to prevent it from freezing. The European forest elephant grew up to 13.8 feet (4.2 meters) tall and weighed 6-11 tons – which is significantly larger and heavier than the African steppe elephant.
How to Count African Forest Elephants
In the dense forest it is not easy to count animals, so scientists simply count their droppings and estimate the number of animals.
Dwarf Elephants
Are there African pygmy or dwarf elephants? This question puzzled zoologists for a long time. Over time, small elephants with a shoulder height of only 4 feet (120 cm) have been discovered in the African forest elephant's habitat. However, researchers found out that the animals do not represent a species of its own. They are more likely to be young animals or have not been able to develop as well due to illness.
The Forest Elephant Is Related To:
Animals in the Same Biome:
Related Articles:
- Main Characteristics of Elephants
- Animals With an Amazing Sense of Hearing
- Amazing Facts About Animal Teeth