Pigeon
Pigeon Facts
| Size | 12-13.5 in (31-34 cm) |
| Speed | Up to 50 mph (80 km/h); 62-75 mph (100-120 km/h) (short distances) |
| Weight | 10-14 oz (300-400 g) |
| Lifespan | Up to 35 years |
| Food | Grains, seeds |
| Predators | Raccoons, owls, eagles, hawks, opossums |
| Habitat | Worldwide |
| Order | Columbiformes |
| Family | Columbidae |
| Scientific name | Columbidae |
| Characteristics | Primarily move by walking on the ground |
Main Characteristics
When we are thinking of pigeons we usually have the picture of a feral dove in our minds. In fact, the family of pigeons is very large.
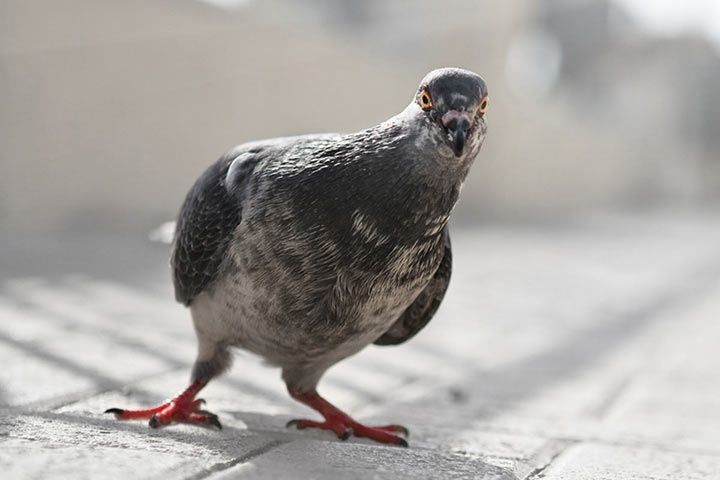

Species
There are more than 300 species. Many of them are very colorful, have beautiful patterns or striking head feathers. Most pigeons live in South Asia to Australia. In Central Europe there are only five species: feral pigeon, common wood pigeon, Eurasian collared pigeon, European turtle dove and stock dove.
Distribution and Habitat
Pigeons prefer forests, but they also live in cities. Only a few species inhabit mountain and desert areas.

Anatomy and Appearance
The Largest
The largest Pigeon is the Victoria crowned pigeon with a weight of more than 4.4 pounds (2 kg) and a size of up to 29 inches (73 cm).
The Smallest
The smallest species is the plain-breasted ground dove. It's just as small as a sparrow and weighs only 0.7 ounces (22 grams).
Feral Pigeons
Feral pigeons grow to 12-13 inches (31-34 cm) and weigh 10-14 ounces (300-400 grams).

Behavior
Eating
Pigeons move on foot very often. As they walk around, they pick up grains and seeds. But unlike many other birds, they can't remove the outer shell of the seeds. They have to swallow them in whole. Another behavior that makes them different from other birds is, that they rarely use their feet when eating.
Drinking
Have you ever watched a bird drinking? It dips its beak into the water and then moves its head back so that so that the water can run down its throat. The bird does not have muscles for swallowing and there is no other way to get fresh water. Pigeons have a different method. They use their beak like a straw to suck water.

Senses and Abilities
Sense of Vision
Pigeons have very good eyesight. They can clearly see objects that are 22 miles (35 km) away - when there are no clouds in between. Like humans they can recognize colors, but they also perceive ultraviolet light.
Speed
Letter pigeons can reach speeds of up to 75 mph (120 km/h).
Magnetic Sense
How does a pigeon find its way home, particularly over unbelievably long distances? It uses the earth’s magnetic fields for orientation.
Flying Distance
Some pigeon species are especially cultured and trained to find their way back home. These pigeons are able to cover distances of more than 620 miles (1,000 km).
Intelligence
An international team of scientists at the Duke University, North Carolina, USA, found out that pigeons can memorize up to 725 patterns for several years. On photos they can recognize a particular person even in different clothes.
Pigeons are also very good at multitasking. They can quickly switch between different two different tasks or puzzles. Even faster than humans.
Pigeons love to gamble. They do it even though they know they could lose their bet (= food). There are only a few other animal species are known to show play behavior, such as primates and dolphins.
They also have a similar understanding of time and space as chimpanzees.
Importance to the Ecosystem
Pigeons eat seeds and spread them around which helps plants to reproduce in new locations. Pigeons are also an important source of food for birds of prey such as the peregrine falcon, the kestrel and the sparrowhawk.
- Find Out More:
- The Fastest Birds