Hamster
Hamster Facts
| Size | Dwarf hamsters: 2-6 in (5-15 cm); European hamster: up to 13 in (34 cm) |
| Speed | Up to 3.7 mph (6 km/h) |
| Weight | 0.8-23 oz (24-650 g) |
| Lifespan | 2-3 years |
| Food | Seeds, grains, fruits |
| Predators | Owls, weasels, falcons, foxes, snakes |
| Habitat | Syria, Europe, Siberia, Mongolia, China |
| Order | Rodents |
| Family | Cricetids |
| Scientific name | Cricetinae |
| Characteristics | Small rodent, short tail |
Main Characteristics
Hamsters are closely related to voles, lemmings and mice. There exist about 20 species – from dwarf hamsters to golden hamsters and European hamsters.
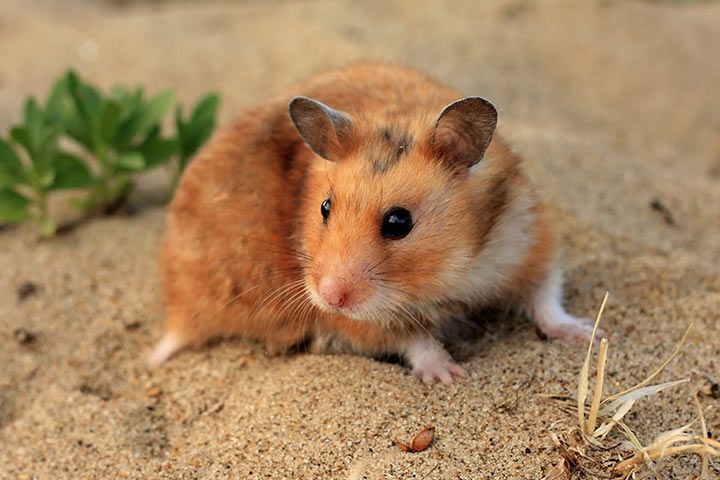

Anatomy and Appearance
Size and Weight
With a length of up to 13 inches (34 cm) and a body weight of up to 23 ounces (650 grams), the European hamster is the biggest species. The smallest is the dwarf hamster Phodopus with a length of 2-4 inches (53-102 mm) and a weight of 0.8-1.5 ounces (24-45 grams).
Cheek Pouches
Hamsters have stretchy cheek pouches. They can stuff in there anything they don't want or can't eat at the moment. The cheek pouches can grow two to three times the size of the hamster's head!
Fur
The European hamster is easy to spot. It usually has a tawny back and a dark belly. There are white spots on his face, front legs and sides. Pet hamsters are colored differently. Syrian hamsters have black markings on the back of their heads and a white belly. Dwarf hamsters are gray, brown, white, cream, piebald, and may have a dorsal stripe.
Teeth
Like most rodents, hamster teeth never stop growing. They wear out as they eat.
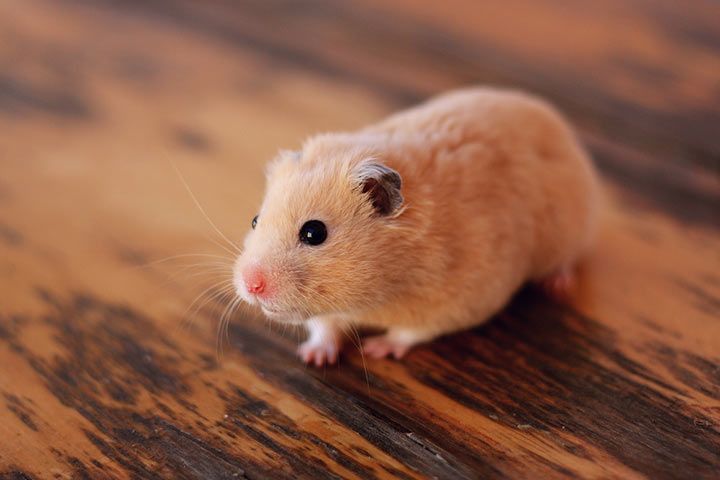

Habitat
Wild hamsters mainly live in arid or semi-arid open grasslands. But they can also be found in forests, steppes, semi-deserts or even in the mountains. The European hamster prefers loess and clay soil.
Diet
Hamsters feed primarily on seeds. But they also eat sprouts, roots, fruits and leaves. The European hamster prefers grain, clover, potatoes and corn. However, hamsters are not strictly herbivores. To a small extent, they also feed on animals such as insects, lizards, frogs.
Life Style
Hamsters are mostly loners. During the day they sleep. They become active at night. They spend most of their time foraging for food supplies and building their burrow.
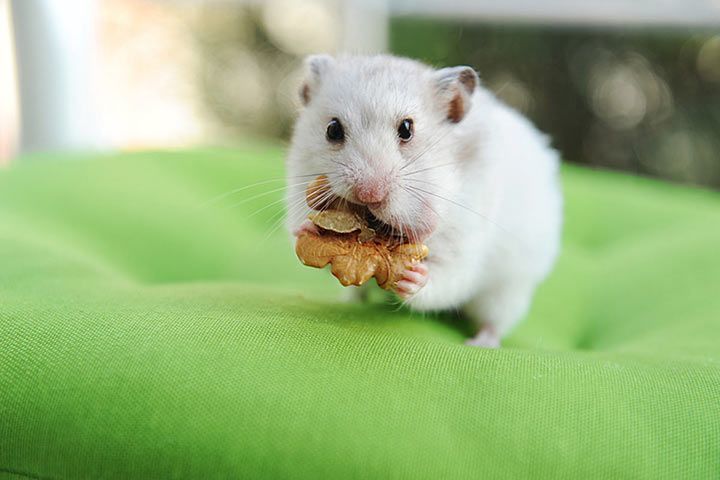

Senses and Abilities
Sense of Smell
Hamsters have an excellent sense of smell.
Eyesight
They're basically „blind as a bat“. They can just see objects up to a distance of 6 inches (15 cm). They perceive movements and differences in brightness. In addition to this, the little animals are color blind.
Sense of Hearing
Hamsters have a well-developed sense of hearing. Their large auricles help direct sounds into their ears.
Sense of Touch
Hamsters have long whiskers. They help them perceive their surroundings and find their way in the dark.
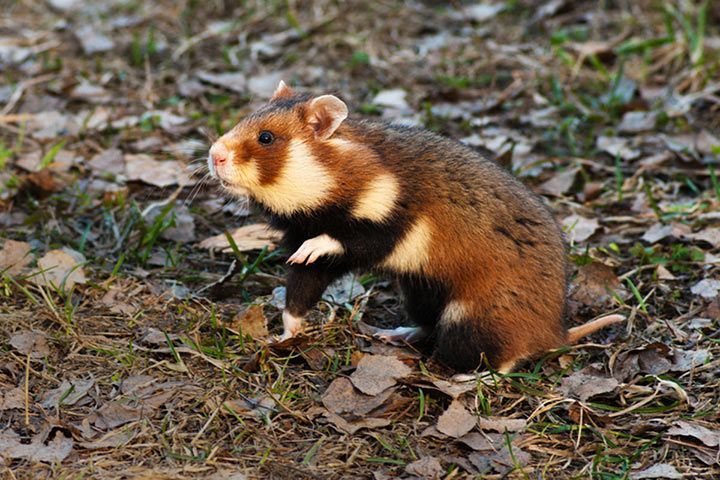

Behavior
Exploring
When they dare to explore unknown areas, they rub their bodies on all kinds of things. This is similar to Hansel and Gretel. While the fairy-tale characters leave bread crumbs as a trail, hamsters leave a scent trail. Following this trail is a piece of cake for them because they have a very fine sense of smell.
Digging
Hamsters love to dig. They spent a lot of time doing so.
Scent Marking
Hamsters leave droppings here and there. This has nothing to do with impurity. This is how the animals mark their territory. They also rub their scent glands on objects. This is called scent marking or flank marking.
The Burrow
Hamsters make burrows for protection from predators and for resting. They are between 20 inches (50 cm) and 6.5 feet (2 meters) underground.
Entrance and Exit
Hamsters create multiple entrances and exits in the wild. There are steep drop tubes that help getting quickly into the burrow when it's on the run. The exit is rather flat.
Chambers
Hamsters like to make their cave nice and cozy. It has a cozy sleeping chamber that is padded with grass. There is also a pantry that is filled to the ceiling. The hamster doesn't even forget a toilet when building its burrow, because it doesn't like bad smells in its home.
During the Winter
What do hamsters do in winter? Pet hamsters do not hibernate because they live in a warm apartment. So what about the wild hamsters that live outside?
It's different with the field hamster, which lives outside in the wild. When it gets colder in autumn, it stocks up its supplies for the cold season. It marches up to 7.4 miles (12 km) in one night. In its shopping ... er ... cheek pouches, it carries up to 11 pounds (5 kg) of food into its burrow.
As soon as the treasures are safely stowed away, it goes one floor down where it is protected from frost during the winter. Then the European hamster starts its well-deserved hibernation. Its pulse drops from 400 beats per minute to four. Its body temperature also drops: from 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 degrees Celsius) to 39 degrees Fahrenheit (4 degrees Celsius). Every few days it wakes up and enters its pantry to enjoy a tasty meal.
Enemies and Threats
Natural predators
The hamster's biggest enemies are weasels, birds of prey and foxes.
Human Impact
The European hamster has been classified as "critically endangered" since 2020 (as of November 2023; no more recent data available). Some of the reasons for this are habitat loss, climate change, light pollution, agriculture and monoculture (agriculture with only one crop species). All of this is caused by humans.
Life Expectancy
Hamsters live two to three years in the wild. As pets, they sometimes live a little longer. They can live two to four years. The world's oldest hamster was a pet and lived to be 4.5 years old.
Reproduction
Hamsters usually mate between April and May - depending on how warm it is and where they live. The gestation period lasts 18-20 days. The babies are born naked and blind. 3-15 babies can be born in one litter. They are nursed for three weeks. After about four weeks they are considered mature.
Evolution and Origin
All golden hamsters originate from the Syrian hamster.
The Hamster Is Related To:
- Gerbil
- Jerboa
Animals in the Same Biome:
- Badger
- Barn Owl
- Eurasian Jay
- Great Spotted Woodpecker
- Hedgehog
- Lynx
- Magpie
- Microbat
- Mouse
- Raccoon
- Raven
- Red Fox
- Wolf
- Find Out More:
- Hamster Breeds (Pet Section)
- Watch Now on animalfunfacts.net:
 All About Hibernation
All About Hibernation