Lion
African Lion Facts
| Size | Up to 3.7 ft (115 cm) (shoulder height) |
| Speed | Up to 37 mph (60 km/h) |
| Weight | Up to 551 lb (250 kg) |
| Lifespan | 8-15 years |
| Food | Antelopes, zebras |
| Predators | - |
| Habitat | Tropical Africa, West India |
| Order | Carnivore |
| Family | Cats |
| Scientific name | Panthera leo |
| Characteristics | Big cat, male with thick mane |
Main Characteristics
Lions are big cats that live in the savannas, dry forests and deserts of Africa. Unlike other cats, lions live in prides and are mostly nocturnal. They prey on medium to large sized ungulates.
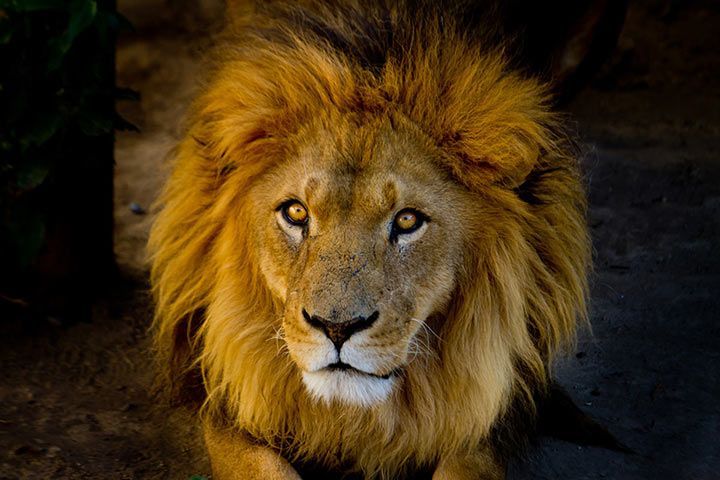

Life Style
Lions are most active at night to hunt for prey. During the day they rest, drink at nearby waterholes and take long naps in the shade of trees and bushes. They sleep up to 22 hours! Each pride has a large territory that is defended against other prides. The boundaries are marked by urine, feces, scratch marks and roars.
Anatomy and Appearance
The Biggest Cat (?)
The King of Animals? For many people, the lion is the most impressive cat. But in fact, it's not the biggest cat. This honor goes to the Siberian tiger. The lion is the second largest.
Size and Weight
African lions have an average body length of 62-74 inches (160-190 cm) and a weight of 260-440 pounds (120-200 kg). The tail is 27-41 inches (70-105 cm) long. How big and heavy a lion is depends on what sex it is, where it lives and what subspecies it belongs to. The females, for example, are always smaller and lighter, the males larger and heavier. In individual cases, males can even have a body length of over 78 inches (200 cm) and weigh up to 550 pounds (250 kg).
Mane
Why do male lions have manes? In the past it was believed that the mane protects against injuries when two males fight each other. But the animals usually attack the back and the hind legs. In the end, scientists found that the mane is all about looks. The darker and longer a lion's mane is, the "prettier" it is for lionesses.
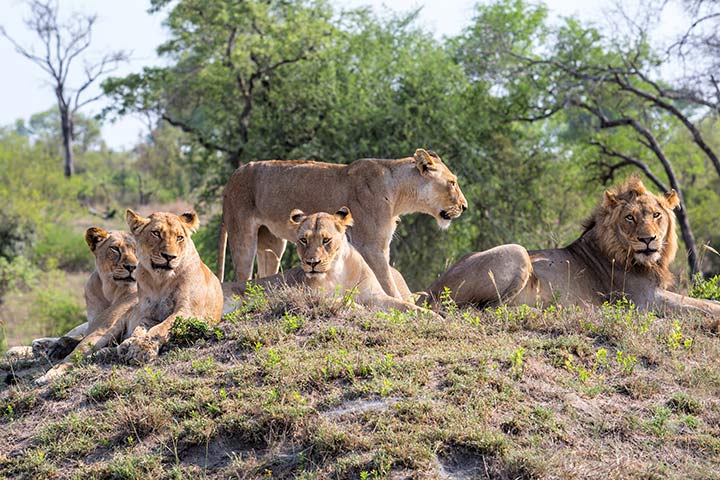

Diet
Prey
Lions prefer medium-sized ungulates such as antelopes, gazelles and zebras, but they also prey on large animals such as wildebeest and buffalos. They rarely hunt elephants, giraffes and hippos because they are too big and too strong. If ungulates aren't available, they include smaller animals such as rabbits, rodents, birds, turtles and crocodiles on their “menu”.
Food Needs
Lions need 11-15 pounds (5-7 kg) of meat per day. In a single meal, they can eat up to 15 % of their own body weight, which can be 44-66 pounds (20-40 kg). Lions don't chew. They swallow the meat whole because their teeth are made for tearing, not for chewing.
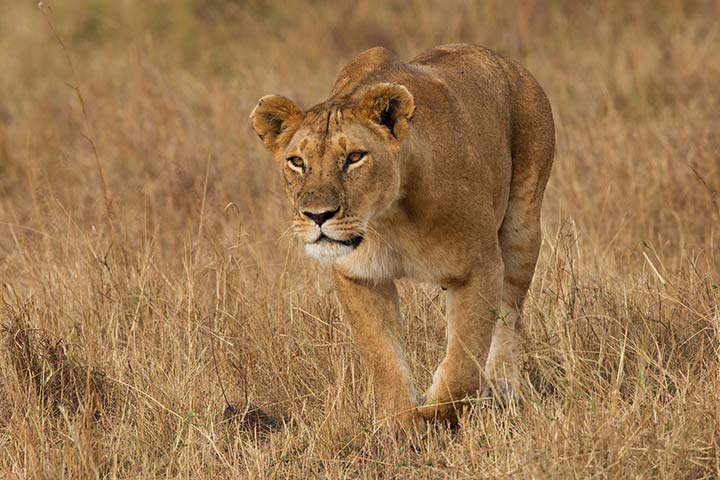

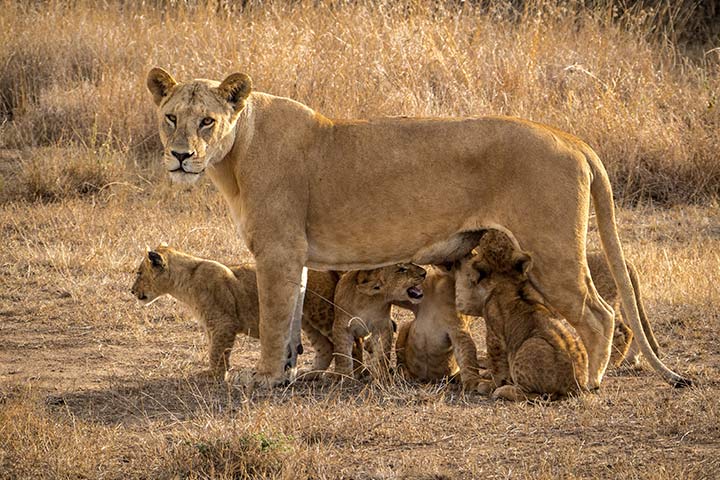
The Pride
Lions are the only big cats that live in groups. A group is called "pride" and it is made up of about 20 animals. It is mainly females and their offspring: mums, grandmothers, sisters, aunts and cousins. Only three to four animals are adult males.
The Role of the Female
The main task of the females is to hunt and take care of the offspring.
The Role of the Male
The male animals hardly ever take part in hunting, but still have important tasks. They mark territory and defend it from invaders. They also protect the offspring while the lionesses hunt.
Life in a Pride
The females remain in the group for their entire lives. But, once the male offspring are two to three years old, they must leave the pride. As long as they haven't found a new one, they team up with other males for sleeping and hunting. To take over a new pride, a male has to prove that it is stronger than everyone else in the pride. It has to defeat all the males. Such a fight happens about every two to three years in every group.

Behavior
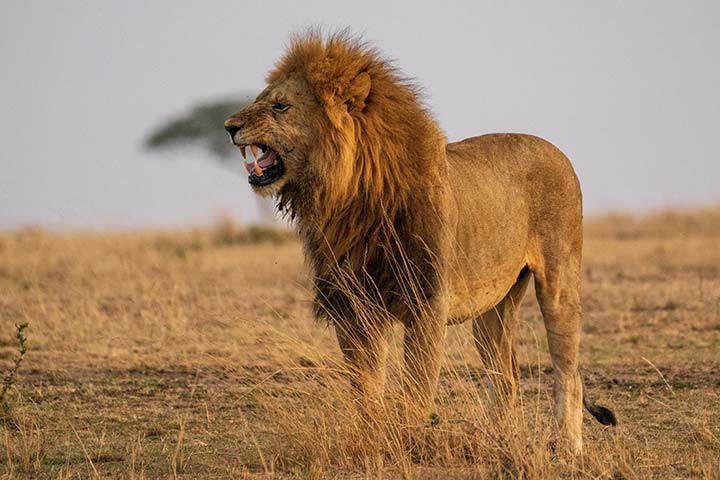
Why Do Lions Roar?
Lions are famous for their roars. They do it to communicate with the pack, but they also use it to intimidate conspecifics from other prides. Both males and females roar. A lion’s roar can even be heard from a distance of 5 miles (8 km).
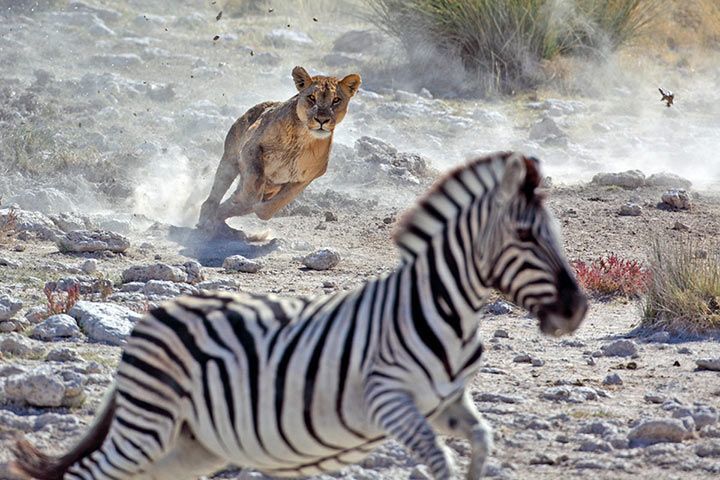
Hunting
When Do They Hunt?
Lions don't hunt during the day. They wait until night, when the weather is cooler and they can't be seen easily. Also, their eyes are much better adapted to night vision than their prey's.
How Do They Hunt?
Lions can run quite fast. They reach a speed of up to 37 mph (60 km/h) over short distances. But antelopes are much faster. They can cover large distances at 60 mph (90 km/h). So what should the lions do? They take advantage of moments of surprise while hunting. They sneak up to their prey from different directions until they are about 30 m away from their victim. During the attack, the prey cannot evade its enemies.

Lion Species
Are There Asiatic Lions?
Yes, there are Asiatic lions, too. They look like their African relatives but their appearance is slightly different. Their mane is shorter and more sparse. Unfortunately, Asiatic lions are threatened with extinction. They survive only in a national park in India. There is a breeding program to save the species. The hope is that it can be reintroduced into the wild sometime in the future.
White Lions
Lions usually have yellowish or light brown fur. There are also white ones, but they are very rare. Their coat color results from a rare mutation in their genes. However, they're not albinos. Albinos lack the color pigments and have red eyes. White lions typically have blue eyes.
Can You Cross a Lion With a Tiger?
Yes, lions and tigers can have offspring. The cross between a male tiger and a female lion is called a tigon. If the male is a lion and the female a tiger, it's called a liger.
Reproduction
Lions give birth once a year. During the first four to six weeks the cubs stay in their hiding place, until they are strong enough to participate in the life of the pack. After three months, the cubs can follow their mother. With about 12 months, the male offspring start to grow their mane. It takes five years until it's fully grown, though. At the age of two to three years old they are old enough to leave the pride and find a new one themselves.

Fun Facts
Stepping Into the Lion’s Den
We use this idiomatic expression when we think that we are entering a dangerous situation. It derives from the fable "The Old Lion and the Fox": In this story, an old and weak lion pretends to be ill and asks other animals to visit it in its den (because it is too weak to go out) - and eventually then eats them. The fox is the only one that sees through this cunning plan. On the ground, he notices the traces that only lead into the den.
The African Lion Is Related To:
Animals in the Same Biome:
- Watch Now on animalfunfacts.net:
 Why Do Animals Team Up?
Why Do Animals Team Up?